The importance of balancing our glucose levels
Blood sugar or glucose comes from the food we eat. It is also produced by our liver. Glucose is the main source of energy for the body’s cells and is transported through the bloodstream.
We feel our best when our blood sugar is balanced. Why?
Let’s explore that in this article.
Is it essential to balance our glucose levels?
The general answer is YES. Balancing your glucose is critical to living a healthy life, whether you have prediabetes, type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, or another type of diabetes.
Or even if you don’t have diabetes.
In people without diabetes, every glucose spike increases the risk of heart disease. Therefore, in the long term, keeping balanced glucose levels will reduce the risk of Alzheimer's disease, fatty liver disease, and cancer.
Why you should avoid spikes even if you don’t have diabetes
If you want to maximize performance and improve energy crashes
Have you ever felt extremely tired after a meal?
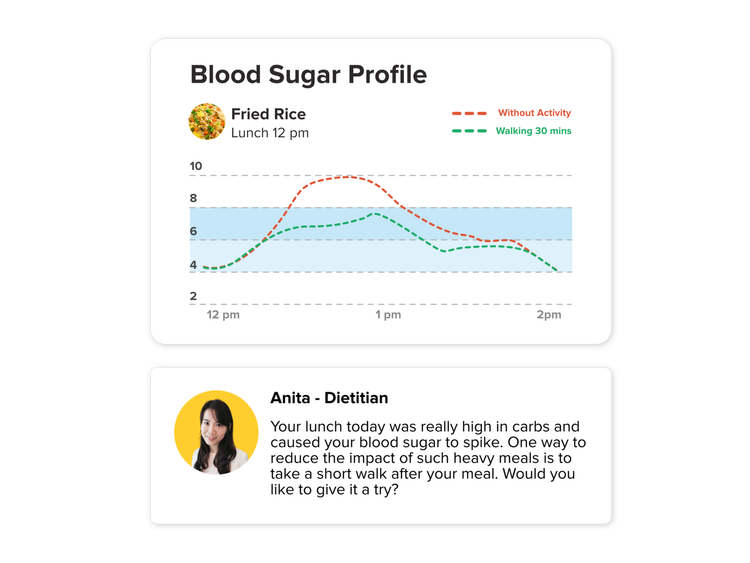
This post-meal slump is something most of us have experienced at some point. This is because after consuming a high-carb meal, your blood glucose is elevated (the “spike”), which gives you a burst of energy.
Your body then releases insulin to lower your blood sugar, which then causes you to feel tired (“crash”). This process is called reactive hypoglycemia. The more the insulin released, the more pronounced the crash will be – to the extent that you feel sleepy after a high-carb meal. Refined carbohydrates, or simple carbs, cause the biggest blood glucose spike – which then requires high amounts of insulin to be released, therefore causing a hefty post-meal slump.
If you want to improve your mood
Did you know that blood sugar fluctuations could negatively impact your mood?
Refined carbs are digested and absorbed into the bloodstream really quickly (compared to complex carbohydrates). This leads to a rapid and dramatic spike in blood sugar levels, resulting in an initial jolt of energy and a corresponding uplift in your mood soon after eating.
However, this doesn’t last. The body will then secrete insulin to counter the rise in blood sugar levels. As insulin levels “catch up” in response and peak, blood glucose levels will fall quickly. Essentially, this creates a “crash and burn” effect associated with symptoms like fatigue and irritability.
Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) has been associated with "nervousness", and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) with "anger or sadness".
These blood sugar fluctuations affect your mental well-being – but it also extends beyond just your mood. It is also associated with chronic fatigue, linked to a higher risk of depression.
If you want to slow down aging and have clearer skin
Aging skin? Acne problems?
Balancing your glucose helps slow down glycation (aging), and even helps with certain skin conditions.
Research has found that elevated blood sugar levels translate to higher levels of certain hormones such as IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor 1). Unfortunately, IGF-1 has been revealed to predispose some people to acne.
Higher sugar levels can also cause collagen damage due to glycation (aging).
Elevated levels of sugar can attach to proteins in the skin to form harmful molecules called advanced glycation end products or AGEs.
Collagen and elastin fibers are the proteins in the skin that are most impacted by AGEs. The process of glycation results in cross-linking of these fibers, leading them to be less resilient and less elastic (the ability of our skin to stretch and bounce back).
In addition, our bodies lose the ability to repair collagen that has been glycated, resulting in a loss of skin elasticity. Loss of skin elasticity accelerates sagging and wrinkling.
Stopping sugar spikes can help reduce glycation and mitigate its negative effects, therefore protecting collagen and slowing down skin aging.
If you have excess weight
Balancing your glucose levels can help you lose weight.
You may have heard of people who have gone on a low carbohydrate diet or have gone through intermittent fasting (IF) and have quickly lost weight.
This is because by fasting, they are able to keep their blood glucose balanced and stable by giving the body a chance to rest and allowing insulin to drop significantly.
Without the insulin spikes, it is much easier to keep the weight off since insulin is our body’s main anabolic hormone – meaning insulin promotes “building” in the body such as storing fat.
Insulin dictates our body to take up glucose from the blood for use, or, to store it if it’s an “excess”.
Weight loss requires us to burn through fat stores, so we also need to control our insulin to tell the body that it should burn fat rather than to hold on to more of it.
In a Nutshell: What happens when there is a glucose spike?
HARMFUL FREE RADICALS
When we spike, our mitochondria become overwhelmed and start producing chemicals called free radicals. Free radicals are harmful for our cells and mutate our DNA.
INFLAMMATION
This leads to oxidative stress and inflammation. Inflammation is the root cause of most diseases. Three out of five people will die of an inflammation-based disease.
AGING
Every glucose spike leads to glycation (the aging process of our body). Glycation leads to many age-related issues, including Alzheimer’s. When we slow down glycation, we live a longer, healthier life.
INSULIN AND FAT GAIN
With every glucose spike, insulin gets released. The excess glucose gets stored in our liver, muscles, and fat cells. A study has shown that adverse consequences currently attributed to obesity could be attributed to hyperinsulinemia (unhealthy high amount of insulin in the blood). This could be one of the reasons we gain fat.
What should your normal glucose range be, as an individual without diabetes?
“Normal” blood glucose level refers to the blood sugar quantity in the majority (95%) of healthy individuals.
Table 1: Reference ranges for fasting and post-meal blood glucose levels
| Fasting Blood Glucose Levels | 2-hr Post Meal Glucose Levels | |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | <5.6 mmol/L (<100 mg/dL) |
3.8 to 7.7 mmol/L (70 to 139 mg/dL) |
| Pre-diabetes | 5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L (100 to 125 mg/dL) |
7.8 to 11.1 mmol/L (140 to 200 mg/dL) |
| Diabetes | ≥7.0 mmol/L (≥125 mg/dL) | ≥11.1 mmol/L (≥200 mg/dL) |
However, “normal” does not necessarily mean that this range is optimal. The glucose cut-offs outlined in the table are used as cut-offs for diagnosis of diabetes. Studies in healthy populations indicate that the average glucose levels are lower than the targets set by most guidelines, and that increases in fasting blood glucose levels can increase the risk of diabetes and heart disease complications.
The “Optimal” Glucose level is the more stringent target, for healthy individuals to strive for – for better metabolic health. Read more about the Optimal glucose level here.
Do you see why it’s important to balance your glucose even if you don’t have diabetes or prediabetes?
Several studies* have shown that these are some of the benefits of balancing your glucose levels, among others:
Better sleep and energy. Steady glucose levels means that you get less insulin spikes – so you don’t often experience a “crash” or sluggishness after meals. In addition, low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, can cause sleep problems. With stable glucose levels, you get better sleep – and more energy throughout the day.
Better mood. Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) has been associated with "nervousness", and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) with "anger or sadness". Balancing your glucose improves your mental well-being.
You lose weight. A balanced and stable blood glucose gives the body a chance to rest and allows insulin to drop significantly. Without the insulin spikes, it is much easier to keep the weight off since insulin is our body’s main anabolic hormone.
Clearer skin. Balanced blood sugar levels means lower levels of IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor 1) which predisposes some people to acne.
Slower aging and fewer wrinkles. Higher sugar levels can also cause collagen damage due to glycation (aging). Stopping sugar spikes can help reduce glycation and mitigate its negative effects, therefore protecting collagen and slowing down skin aging.
A healthier life, in general. The variability caused by these glucose spikes can lead to the activation of oxidative stress, which is one of the main factors for cardiovascular diseases.
How can NOVI help?
You may feel healthy, but did you know that the majority of the working population in Singapore is affected by excess weight and chronic metabolic conditions? According to the National Population Health Survey 2017, Another 1.5 in 4 Singaporeans are overweight or at-risk of developing a chronic lifestyle condition.
If you are feeling sluggish, feel that your mood swings are affecting your work, suffer from certain skin conditions, or need help to lose weight, we can help you find the most appropriate ways to stabilize your glucose levels.
NOVI offers health solutions that are personalized to meet your unique needs so it is easier for you to achieve your health goals.
Invest in a healthier you.